What is Claudication?
Technically, claudication is a symptom of Peripheral Arterial Disease (P.A.D.), that is characterized by pain and fatigue in the legs, usually during an activity such as walking. Tiredness or pain in the legs typically begins when you start exercise and goes away shortly after resting.What Causes Claudication?
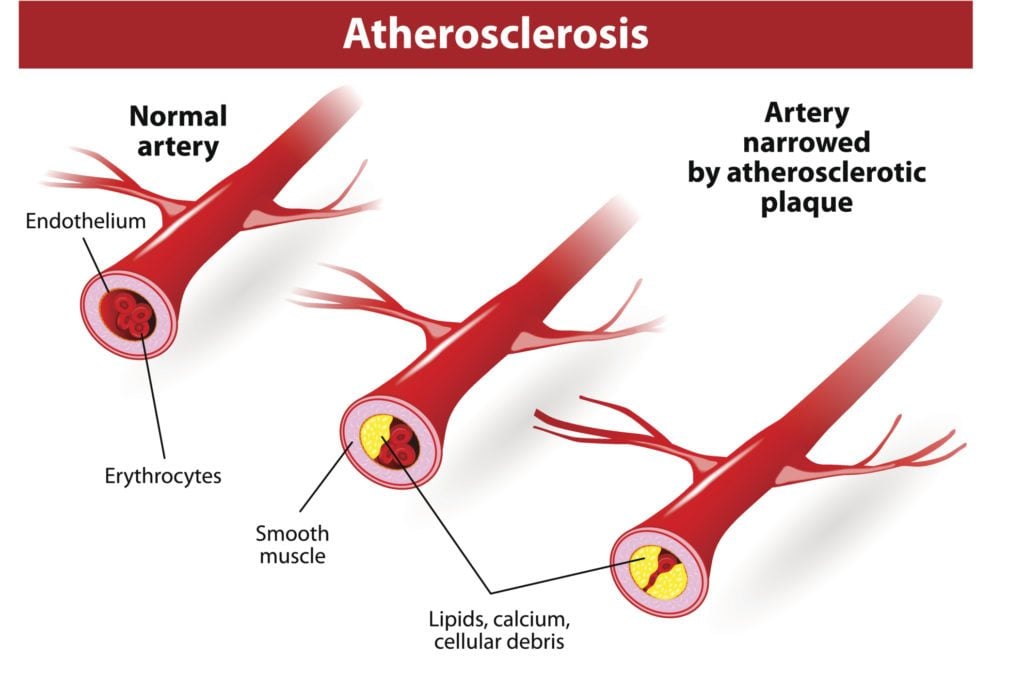 Claudication is caused by a narrowing, blockage in the arteries that carry blood to your legs. As a result of blockage, the leg muscles do not receive enough blood or oxygen to support physical activity. The lack of oxygen in the muscles can cause pain, tingling or a feeling of tiredness.
A narrowing or hardening of the arteries is called atherosclerosis, which can develop in any of your arteries. When you have atherosclerosis in the arms or legs, it is called peripheral arterial disease, better known as P.A.D.
Claudication is caused by a narrowing, blockage in the arteries that carry blood to your legs. As a result of blockage, the leg muscles do not receive enough blood or oxygen to support physical activity. The lack of oxygen in the muscles can cause pain, tingling or a feeling of tiredness.
A narrowing or hardening of the arteries is called atherosclerosis, which can develop in any of your arteries. When you have atherosclerosis in the arms or legs, it is called peripheral arterial disease, better known as P.A.D.
Symptoms of Claudication
- Depending on the location of the blockage, pain can occur in the feet, calves, thighs, hips or buttocks
- In addition to or instead of pain, you may experience: aching, burning, cramping, heaviness, tightness, tingling, tiredness, or weakness in the legs
- Claudication causes intermittent pain that comes and goes as your level of physical activity changes
- In some cases, blood flow can be severely reduced, causing the toes (or fingers) to feel cold, appear bluish
- Lack of blood flow can also contribute to sores or ulcers on the lower extremities
How is Claudication Treated?
Claudication is one of the most common conditions we diagnose at the Center for Vascular Medicine. There are several tests that we perform for patients who have signs or symptoms of P.A.D. including:- Ankle-brachial index (ABI) - A non-invasive examination performed with blood pressure cuffs on the arms and legs. This test can usually be completed in under 5 minutes.
- Duplex ultrasound - This is also a non-invasive test and considered to be the gold standard for diagnostic evaluation of the arterial system. This test allows our doctors to see how blood is flowing through your vessels, as well as the speed and direction of blood flow.
- Angiography - An angiography is an x-ray of the arteries used to confirm abnormal findings from an ultrasound exam. This diagnostic examination is performed in one of our out-patient offices under light anesthesia.
- Laser Atherectomy - A relatively new technique offered at Center for Vascular Medicine, which reestablishes blood flow through narrowed or blocked arteries. The laser is used during angiographic procedures with minimally invasive techniques.
- Angioplasty - This technique is used to open blocked arteries by inflation of a balloon catheter. This technique is also utilized in the angiography suite, frequently in conjunction with both the laser atherectomy and stenting.
- Stenting - The doctor will insert a cylindrical, metal wire, mesh tube into the artery in order to keep the blood flow channel open. This technique is often combined with the laser atherectomy and angioplasty.
